In today’s hyper-competitive business environment, understanding the forces that shape industry dynamics is crucial for success. Whether you’re a startup founder, corporate strategist, or market analyst, knowing how to apply Porter’s Five Forces can give you a powerful edge. This strategic framework not only reveals the competitive intensity within an industry but also guides informed decision-making to enhance profitability and long-term sustainability.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into Porter’s Five Forces application, exploring what the model is, why it matters, how to apply it step-by-step, and how real companies leverage it to stay ahead. We’ll also address common challenges and reveal modern adaptations that keep the model relevant in a fast-evolving marketplace.
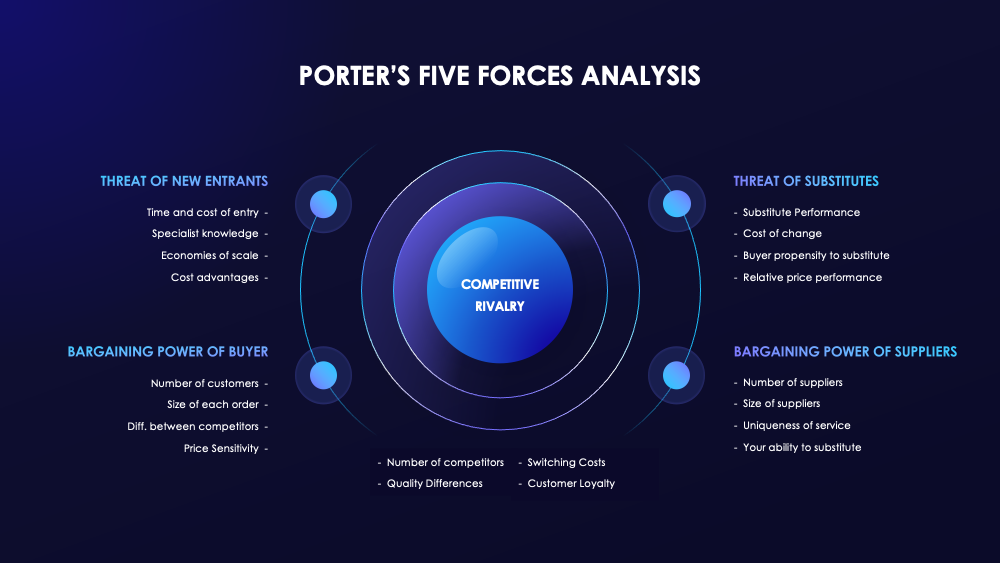
What is Porter’s Five Forces? Understanding the Framework
Developed by Harvard Business School professor Michael E. Porter in 1979, Porter’s Five Forces is a foundational tool in strategic management. It identifies five critical competitive forces that influence an industry’s profitability and structure. By analyzing these forces, businesses can understand the pressures they face, identify opportunities, and develop strategies to strengthen their market position.
The Five Forces Explained
-
Threat of New Entrants
This force examines how easy or difficult it is for competitors to enter the industry. High entry barriers (like capital requirements, regulation, or strong brand loyalty) reduce this threat, protecting existing companies. -
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
When suppliers have significant power, they can demand higher prices or limit quality, squeezing industry profitability. Factors increasing supplier power include few suppliers, unique inputs, or switching costs. -
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Powerful buyers can force prices down or demand better products, impacting profitability. Buyer power rises when buyers are concentrated, purchase in large volumes, or have access to product information. -
Threat of Substitute Products or Services
Substitutes limit industry potential by offering customers alternatives, often at lower costs or greater convenience. The more viable substitutes, the higher the competitive pressure. -
Industry Rivalry
This encompasses the intensity of competition among existing firms. High rivalry can lead to price wars, advertising battles, and increased innovation—all affecting profitability.
As Porter himself wrote in Competitive Strategy (1980), these forces collectively determine the competitive landscape and guide firms in positioning themselves effectively.
Why Apply Porter’s Five Forces? Benefits and Business Impact
Practical Benefits of the Framework
Applying Porter’s Five Forces goes beyond academic theory—it’s a practical tool with multiple business benefits:
-
Market Insight: Understand structural forces shaping your industry to anticipate changes.
-
Strategic Planning: Identify threats and opportunities to inform product development, pricing, and marketing strategies.
-
Competitive Advantage: Recognize where your company can exert influence and protect profit margins.
-
Risk Management: Prepare for potential disruptions from new entrants or substitutes.
A 2023 McKinsey report found that companies systematically using competitive analysis frameworks like Porter’s Five Forces outperform their peers in profitability by up to 15%.
Real-World Impact
Consider Apple Inc., which applies Porter’s framework to maintain its dominance. Apple carefully manages supplier relationships to ensure quality while protecting against supplier power, innovates continuously to mitigate substitute threats, and fiercely competes in a highly rivalrous tech industry.
For startups, understanding entry barriers and buyer power is critical to carving out a sustainable niche.
Step-by-Step Guide to Applying Porter’s Five Forces
A systematic approach to applying Porter’s Five Forces ensures comprehensive and actionable insights. Here’s how to conduct the analysis effectively:
1. Define the Industry Scope
Clarify the boundaries of the industry you’re analyzing. Consider geographic reach, product/service range, and market segments.
2. Research Each Force
Collect data on each force using:
-
Industry reports (e.g., Gartner, Deloitte)
-
Competitor analysis
-
Supplier and buyer interviews
-
Market trends and customer feedback
3. Assess the Intensity of Each Force
Evaluate how strongly each force affects industry profitability:
-
Rate the threat level (low, medium, high)
-
Identify key drivers influencing each force (e.g., number of suppliers, buyer concentration)
4. Identify Strategic Actions
Based on the analysis, develop strategies to:
-
Raise entry barriers or lower threat from substitutes
-
Negotiate better terms with suppliers and buyers
-
Differentiate offerings to reduce rivalry impact
Tools and Resources
Leverage tools such as SWOT analysis, PESTEL analysis, and market intelligence platforms (e.g., SEMrush, Ahrefs) to supplement your research.
Applying Porter’s Five Forces in Different Industries
The model’s application varies by industry. Here are some illustrative examples:
Technology Industry
-
Entry Barriers: High due to significant R&D investment and intellectual property.
-
Supplier Power: Moderate; depends on chip manufacturers and software providers.
-
Buyer Power: Moderate to high due to wide options and low switching costs.
-
Substitute Threat: High, with rapidly evolving alternatives (e.g., cloud vs on-premise).
-
Rivalry: Intense, with competitors like Apple, Google, Microsoft.
Example: Amazon uses Porter’s Five Forces to analyze cloud computing market dynamics, balancing supplier relationships and pricing strategies to dominate AWS.
Retail Industry
-
Entry Barriers: Moderate; online platforms have lowered entry barriers.
-
Supplier Power: High in niches with few suppliers; low for commoditized products.
-
Buyer Power: High, especially with price-sensitive consumers and easy online price comparisons.
-
Substitute Threat: Moderate to high due to alternate shopping channels.
-
Rivalry: Very intense with giants like Walmart and Alibaba.
Healthcare Sector
-
Entry Barriers: Very high due to regulatory compliance and R&D costs.
-
Supplier Power: High for specialized drugs or equipment suppliers.
-
Buyer Power: Variable; insurance companies and government entities wield significant power.
-
Substitute Threat: Moderate with emerging telemedicine and alternative therapies.
-
Rivalry: Moderate but increasing with new biotech entrants.
Common Challenges When Applying Porter’s Five Forces and How to Overcome Them
1. Data Scarcity or Inaccuracy
Gathering reliable data can be tough, especially in niche or emerging industries. Overcome this by:
-
Using multiple data sources
-
Conducting primary research (surveys, expert interviews)
-
Leveraging AI tools to analyze market data
2. Subjective Assessment
Rating force intensity often involves judgment calls. Reduce bias by:
-
Involving cross-functional teams
-
Using quantifiable metrics wherever possible
-
Validating findings against industry benchmarks
3. Rapidly Changing Markets
Porter’s model was developed in a relatively stable industrial context. Today’s fast-changing markets require:
-
Frequent updates to analysis
-
Combining with agile strategic frameworks
-
Incorporating digital tools for real-time monitoring
Advanced Applications and Modern Adaptations
Integrating with Digital Transformation
Modern companies combine Porter’s Five Forces with digital analytics to monitor competitive threats in real time. For example, AI-driven market intelligence platforms can flag emerging substitutes or shifts in buyer behavior.
Sustainability and ESG Factors
Environmental and social governance criteria increasingly influence supplier and buyer power, regulatory threats, and substitute development. Forward-thinking firms now apply Five Forces with a sustainability lens to future-proof strategy.
Combining with Other Frameworks
-
SWOT Analysis: Use Porter’s insights to inform strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
-
PESTEL Analysis: Understand external macro factors influencing the five forces.
-
Blue Ocean Strategy: Identify uncontested market spaces beyond the forces.
Conclusion
Porter’s Five Forces remains one of the most powerful tools for understanding industry competition and guiding strategic decisions. Its application enables businesses—from startups to multinational corporations—to identify threats, capitalize on opportunities, and sustain competitive advantage. By applying this framework systematically and adapting it for modern challenges like digital disruption and sustainability, companies can navigate complexity with confidence.
Ready to apply Porter’s Five Forces to your business? Download our free comprehensive worksheet to get started, or sign up for our upcoming webinar where industry experts walk you through real-world applications. Don’t miss the opportunity to transform your competitive analysis and strategy.
FAQ
Q1: What is the most important force in Porter’s Five Forces?
It varies by industry. Often, industry rivalry or buyer power has the biggest impact but analyzing all forces together provides the full picture.
Q2: Can startups benefit from Porter’s Five Forces?
Absolutely. Startups can assess entry barriers and competitive threats to develop effective market entry strategies.
Q3: How often should I update my Porter’s Five Forces analysis?
Ideally, annually or whenever there’s significant market change, such as new competitors, regulations, or technological shifts.
